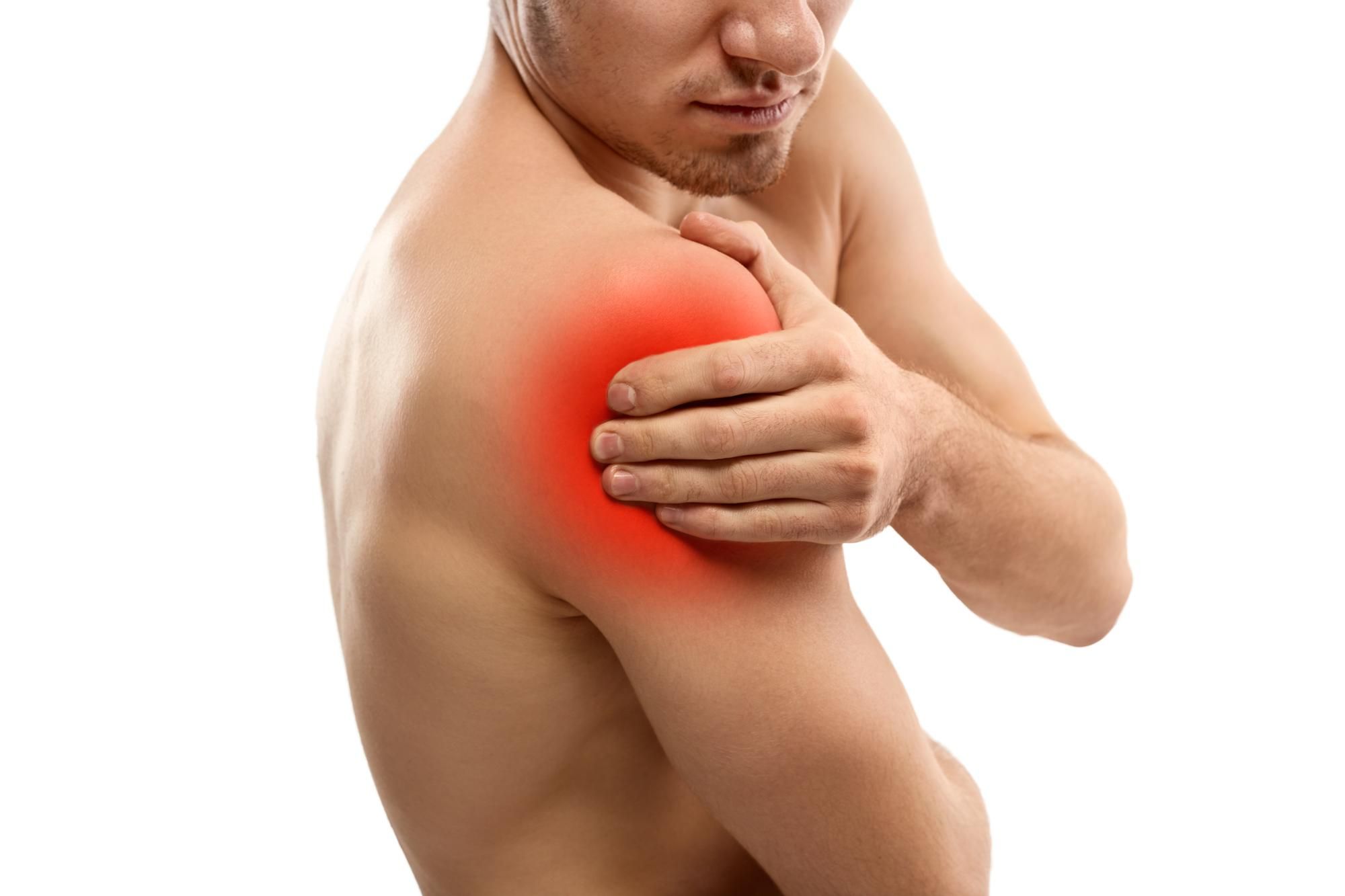
Shoulder bursitis is the inflammation of small, fluid-filled sacs known as bursae that cushion the tendons and muscles near their attachments to the shoulder joint. These bursae work to enable smooth movement of the joint, but when inflamed, they lead to pain and limited mobility.
Due to inflammation and pain, movements between the muscles and tendons are restricted. Practically any age group can be affected, though it is more commonly seen with overuse as in athletes or degeneration in old age.
What is Shoulder Bursitis?
The shoulder joint, a complex structure involving bones, tendons, and muscles, relies on the synergy of various components for seamless movement. Among these components, the bursae play a crucial role. They are in place to cushion the various components of the joint, ensuring smooth gliding of one structure over the other.
Types of Shoulder Bursitis
There are three types of shoulder bursitis:
- Chronic: This happens when shoulder bursitis keeps coming back, usually due to repeated injuries or overusing the shoulder. It’s the most common type.
- Acute: This type happens suddenly after an injury, but it is just a one-time problem.
- Infectious (septic): This occurs when an infection from another part of the body spreads to the shoulder area and affects the bursa.
Causes and Symptoms of Shoulder Bursitis
Injuries and excessive use of the shoulder are the main reasons for bursitis. This happens a lot with sports injuries or when one repeatedly strains the shoulder. The most common symptoms are:
- Shoulder pain
- Swelling
- Redness or Discoloration on the skin
- Stiffness
- Reduced range of motion (stiffness)
- Tenderness to even a light touch
- Feeling heat or warmth
What are the risk factors?
Anyone can get shoulder bursitis, but one is more likely to get it if:
- Do physical work that puts a lot of pressure on the shoulders, like using tools or lifting heavy things.
- Play sports that require moving the shoulder over and over, like throwing, rowing, or swinging a bat, racket, or club.
- People like painters, carpenters, landscapers, plumbers, and warehouse workers have a higher chance of getting it.
- Have a health problem that causes swelling in the body.
Diagnosis for Shoulder Bursitis
If one suspects shoulder bursitis, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial. Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination and may include tests like:
- A musculoskeletal ultrasound of the shoulder to find swelling between the muscles.
- Blood tests to look for indicators of infections.
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) or ultrasound to examine for inflammation in the bursae and/or damage in other areas of the shoulder.
- Joint aspiration to extract and analyse fluid from the bursae for infections or gout.
Management and Treatment For Shoulder Bursitis
Pausing activities that strain your shoulder will allow it to heal properly. Your healthcare provider will advise you on how long you should rest and refrain from physical activities. Additional treatments for shoulder bursitis include:
- Cold therapy: Applying ice to your shoulder can assist in alleviating symptoms. Use an ice pack several times a day for about 15 minutes, making sure to wrap it in a thin towel or cloth to prevent direct contact with your skin.
- OTC pain medications: Using over-the-counter NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) or acetaminophen can help relieve pain and diminish inflammation. Avoid taking these medications continuously for more than 10 days without consulting your healthcare provider.
- Injections into the Bursa: A pain physician may inject a local anaesthetic with a small quantity of steroids into the bursa to reduce inflammation related to bursitis.
- Physical therapy (PT): Participating in PT can aid in strengthening your shoulder muscles and improving flexibility. This can assist in managing bursitis symptoms and preventing future injuries.
- Antibiotics: If you have infectious bursitis, you will need antibiotics. It’s important to complete the entire course of antibiotics as prescribed by your healthcare provider, even if you start feeling better.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How can Bursitis be Prevented?
Incorporating proper warm-up routines, maintaining good posture, and practising shoulder-strengthening exercises can reduce the risk.
What to do if the symptoms of bursitis do not improve?
If the symptoms of bursitis don’t get better, you should talk to your doctor. Normally, the symptoms should improve with the treatment mentioned earlier.
How to treat Shoulder Bursitis with exercises?
One should focus on gentle stretching and strengthening to improve flexibility and reduce pain in the shoulder. Common exercises for Shoulder Bursitis are wall push-ups, scapular squeezes, and pendulum swings.
What are some of the lifestyle adjustments that can help with bursitis?
The most important factor in prevention is ensuring proper warm-up and avoiding sudden, jerky movements or exercises in sports activities.
Is it safe to take injections into the shoulder joint?
Yes, it is safe to take these injections, provided they are given by a qualified doctor and under image guidance for precise deposition of medicine at the target.